What Is The SCOPE OF SOIL SCIENCE In Details?
What Is The Scope Of Soil Science?
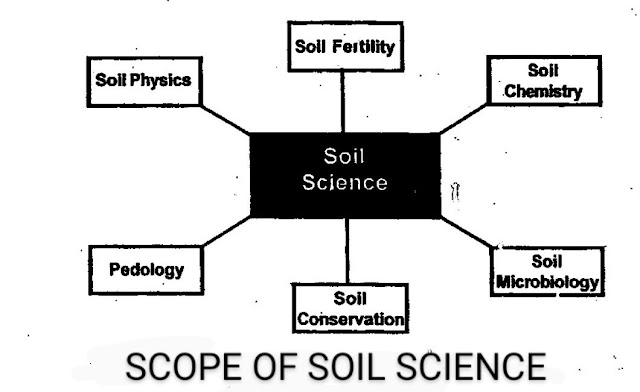
The soil science has six well-defined and developed disciplines. Scope of soil science is reflected through these disciplines.
What Is Soil Science
The science dealing with soil as a natural resource on the surface of the earth, including, Pedology (soil-genesis, classification and mapping) and the physical, chemical, biological and fertility properties of soils and these properties in relation to their managements for crop production.
The soil Science has the following six well-defined disciplines:
1. SOIL FERTILITY
: It denotes the status of a soil with respect to the amount and availability of elements to plant necessary for its growth. Soil fertility, therefore, refers to the nutrient supplying properties of the soil it is bes by considering :-(i) the nutrient requirement of plants;
(ii) the supply of nutrients by the soil,
(iii) ways in which nutrients are lost from the soil, and
(iv) methods by which soil fertility may be maintained or restored.
While, soil productivity is the capacity of a soil,in its natural environment, to produce crops under a specified system of management, and expressed in terms of yield.
In the definition, specifications are necessary, since no soil can produce all crops with equal success nor can a single system of management produces the same effect on all soils.
Hence study of soil science is necessary for maintaining soil fertility.
2. Soil Chemistry
: It is a division of soil science concerned with the chemical constituents, the chemical properties and the chemical reactions of soil.It is the study of chemical composition of soil in relation to crop production.
3. Soil Physics
: Soil physics is a division of soil science that involves the study of physical properties of soil. Soil is a system and is made up of solid, liquid and gaseous materials which affects soil structure.
The chemical and physical relationships among solid, liquid and gaseous phases are affected not only by their own respective properties but also by temperature, pressure and light.
4. Soil microbiology:
Soil microbiology is the science, which deals with microscopic population of the soil, its role in various transformations and its importance in plant nutrition and crop production. Soil micro-biology is concerned not only with soil micro-organisms and classification of soil-inhabiting micro-organisms, but also with measurements of their activities in the soll
These activities are like decomposition of organic materials that are present in the soil or that find their way into the soil, with the production of ammonia, nitrates, fixation of nitrogen and numerous such transformations.
5.Soll conservation:
It is a division of soil science dealing with the protection of soil against physical loss by erosion or against chemical deterioration; that is excessive loss of nutrients by either natural or artificial means. It deals with a combination of all management and land use methods, which conserve the soil against degradation or deterioration by natural or human-induced fac management of the soil with the purpose of producing high yields and, time, protecting it from degradation.
6. Pedology
: The science dealing with the genesis, survey and the laws of geographic distribution of soils as a body in nature.Therefore the study of the scope of soil science is necessary to deal with various problems of soil related to enrichment of soil organic matter , improving soil fertility , plant growth and growing of vegetation . Thus every soil scientist has to study these scopes to understand soil science very well.



Comments
Post a Comment